FAMe
B3D
Biofilms & Spatially Organised Communities
Research activities overview, related to antibioresistance:
- Biofilm-associated tolerance to antibiotics
- Combination of molecules, Resensitivation,
- Cross resistance between biocides and antibiotics
- New antimicrobials
Expertise:
- Live/dead Biofilm structural dynamics by live cell imaging
Main references related to antibioresistance:
- Charron R, Lemée P, Huguet A, Minlong O, Boulanger M, Houée P, Soumet C, Briandet R, Bridier A. Polyhexamethylene biguanide promotes adaptive cross-resistance to gentamicin in Escherichia coli biofilms. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Dec 11;13:1324991. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1324991.
- Tunç MN, Guéneau V, Loux V, Del Campo R, Carballido Lopez R, Briandet R. Genome sequences of four colistin-resistant ESKAPE bacterial strains isolated from patients within the same hospital. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2024 Jan 17;13(1):e0087423. doi: 10.1128/mra.00874-23.
- Charron R, Boulanger M, Briandet R, Bridier A. Biofilms as protective cocoons against biocides: from bacterial adaptation to One Health issues. Microbiology (Reading). 2023 Jun;169(6):001340. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001340.
- Sahli C, Moya SE, Lomas JS, Gravier-Pelletier C, Briandet R, Hémadi M. Recent advances in nanotechnology for eradicating bacterial biofilm. Theranostics. 2022 Feb 28;12(5):2383-2405. doi: 10.7150/thno.67296.
- Boudjemaa R, Steenkeste K, Jacqueline C, Briandet R, Caillon J, Boutoille D, Le Mabecque V, Tattevin P, Fontaine-Aupart MP, Revest M. Live intramacrophagic Staphylococcus aureus as a potential cause of antibiotic therapy failure: observations in an in vivo mouse model of prosthetic vascular material infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2018 Sep 1;73(9):2418-2421. doi: 10.1093/jac/dky205.
- Boudjemaa R, Cabriel C, Dubois-Brissonnet F, Bourg N, Dupuis G, Gruss A, Lévêque-Fort S, Briandet R, Fontaine-Aupart MP, Steenkeste K. Impact of Bacterial Membrane Fatty Acid Composition on the Failure of Daptomycin To Kill Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Jun 26;62(7):e00023-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00023-18.
Keywords:
Biofilms, diffusion-reaction, tolerance/resistance, resensitisation, cross-resistance
BaPS
Pathogenic bacteria and Health
Research activities overview, related to antibioresistance
Our team is working on the pathophysiology of Clostridioides difficile. Our research activities related to the FAMe axis are focused on
- deciphering antibiotic resistance mechanisms of anaerobic bacteria;
- identifying new targets, especially cell wall components;
- developing alternatives to antibiotics (such as mucosal vaccines using surface components or probiotics);
- characterizing bacterial persistence, especially biofilm and its role in recurrence.
Expertise:
- purification and analyses of cell-wall structures
- anaerobic biofilm production and caracterization
- animal models of C. difficile infection (gnotobiotic and conventional)
- genetic manipulation of anaerobic bacteria
- antibiotic resistance in clostridia
Main references related to antibioresistance
- Candela T et al, A cfr-like gene cfr(C) conferring linezolid resistance is common in Clostridium difficile. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2017.03.013
- Lacotte PA et al, Inhibition of in vitro Clostridioides difficile biofilm formation by the probiotic yeast Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 through modification of the extracellular matrix composition. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10061082
- Bruxelle JF, et al, Protection against Clostridium difficile infection in a hamster model by oral vaccination using flagellin FliC-loaded pectin beads. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.08.013
Contact & link:
Claire Janoir-Jouveshomme
Thomas Candela
Keywords : bacterial surface, biofilm, vaccine, probiotics
Bio-RetroSynth
BioRetroSynth
Research activities overview, related to antibioresistance:
PIA Project iCFRee funded by France 2023 for the production and novel antimicrobial peptides and proteins in cell-free systems.
ANR DREAMY project builds mathematical models (deterministic and stochastic) of bacteriophage secretion and infection, for future applications in phage therapy and microbiota engineering.
Expertise:
Main references related to antibioresistance:
Contact & link:
- Manish Kushwaha
- Jean-Loup Faulon
ChemSyBio
ChemSyBio
Research activities overview, related to antibioresistance:
Peptides, including ribosomally-synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs), are promising candidates to develop innovative antibiotics. Indeed, they are generally regarded as specific in order to preserve the human microbiota, safe and to minimally trigger the development of resistance mechanisms.
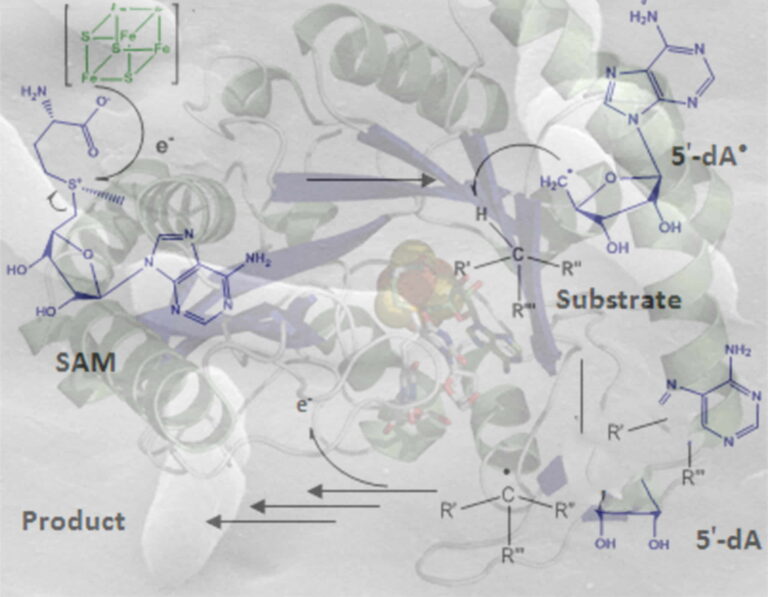
In the ChemSyBio team, we are interested in the discovery of novel RiPPs and the biochemical and structural study of the enzymes involved in RiPP biosynthesis. Our team has identified and characterized novel RiPPs and deciphered their biosynthetic pathway. Notably, we have found key enzymes, radical SAM enzymes, involved in the installation of unprecedented post-translational modifications that confer their bioactivity to numerous RiPPs.
Recent work from our lab has shown that RiPPs and radical SAM enzymes are present in large numbers in the bacteria that colonize humans and make up the human microbiota. Although these bacteria and their genes represent a considerable genetic potential, known as the microbiome, our knowledge is still limited and one main goal of our team is to mime the human microbiome for novel antibiotics.
Expertise:
- Biochemistry, Protein expression and purification, Peptide modification
- Microbiology, Structural analysis
- Mass spectrometry analysis.
Main references related to antibioresistance:
- X. Kubiak et al., Nat Chem Biol (2023) 10.1038/s41589-023-01493-1.
- F. Soualmia et al., Chemistry 28, (2022). 10.1002/chem.202200627
- C. Balty et al., J Biol Chem 294, 14512-14525 (2019). 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009416
- C. Balty et al., J Biol Chem 295, 16665-16677 (2020). 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015371
- C. Balty et al. J Biol Chem 294(40):14512, (2019): 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009416.
- A. Benjdia, A. Guillot, P. Ruffié, J. Leprince, O.
Contact & link:
Keywords: RiPP (ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides), peptides, antibiotics, enzyme catalysis, microbiome, natural products, structural biology
CPE
Commensalism and Pathogenesis of Enterococci
Research activities overview, related to the fight against antibioresistance
Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium, rank among the top five causes of opportunistic infections in humans and Enterococcus cecorum has become a major cause of lameness in poultry. Our research on the molecular, cellular and physiological mechanisms of pathogenesis has led us to investigate novel non-antibiotic preventive or therapeutic strategies against enterococci. We have identified a consortium of commensal bacteria that improves the restoration of the gut microbiota after antibiotic-induced dysbiosis and the barrier effect against vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) in mice. We determined tentative cutoffs for around twenty antimicrobials on a large collection of E. cecorum and isolated virulent bacteriophages in order to develop phage solutions directed against E. cecorum.
Expertise :
Enterococcal genetics, , ecological and cellular microbiology, anaerobic microbiology, phage biology.
Main references related to antibioresistance :
Contact & link:
Keywords : Enterococcus, pathobiont, gut colonization resistance, phages
EpiMic
Epimic
Research activities overview, related to antibioresistance:
The Epimic team studies the molecular basis of persistent bacterial infections by using as a model the facultative intracellular pathogen L. monocytogenes. We have shown that during long-term infection in epithelial cells, Listeria enters a slow-replicating/ quiescent state which is associated with antibiotic tolerance. We are interested in the characterization of the signaling events and the molecular players that regulate the transition between the replicative and dormant state.
Expertise:
Main references related to antibioresistance
PMID: 29190284, 34858876
https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.11.16.566987
Contact & link:
GME
Microbial Genetics and Environment
Research activities overview, related to antibioresistance:
Insect in vivo infection model : Galleria mellonella used to:
- analyze pathogen’s adaptation and growth (eg. explore Bacillus cereus gene expression during infection and exposed to different stresses)
- Pre-screen molecules/organisms to inhibit growth of pathogens (eg. Staphyloccus aureus in collaboration with MicrobAdapt)
Development of quorum-quenching molecules targeting virulence regulators.
The role of biofilm structure/composition in the protection against Clostridioides difficile growth +/- antibiotics
Expertise:
- Bacterial genetics
- Pathogen-host interaction (histology/gene expression)
- Insect model
- Bacterial Biofilm
Main references related to « antibioresistance »
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1959790
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2301045120
Contact & link:
Keywords. Insect infection model, Bacillus cereus, quorum sensing inhibition, Clostridioides difficile, biofilm
MicrobAdapt
MicrobAdapt
Research activities overview, related to antibioresistance:
Staphylococcus aureus is a member of ESKAPE group from World Health Organization. Treatment of S. aureus infections is hampered by the organism’s ability to resist many antibiotics. In the team, we are developing researches into resistance mechanisms: role of exogenous fatty acids, role of phages, role of mutations leading to multi-resistant variants. We are also developing biocaptors for detecting S. aureus in complex environments (food, blood).
Expertise:
- microbiology
- fatty acid analysis
- metabolism
- biochemistry
- electrochemistry
- physiology
- genetic
Main references related to antibioresistance:
- mBio. 2021 Feb 2;12(1):e03193-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03193-20
- ACS Omega. 2024 Jan 4;9(2):2841-2849. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c08219.
- Res Microbiol. 2022 Jul-Sep;173(6-7):103953. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2022.103953.
Contact & link:
Keywords : S. aureus, adaptation, antibiotic resistance, biocaptor, mechanisms.
MuSE
Mutagenesis in Single Cells and Evolution
Research activities overview, related to antibioresistance:
- Characterization of the effect of sublethal concentrations of antibiotics on the bacterial mutation rate through the development of new unbiased methods.
- Study of the consequences of mutation rate fluctuations on the emergence of antibiotic resistance.
- Modulating phage mutation rates for phage therapy
Expertise:
- physiology and genetics of E. coli and its phages, molecular biology
- single-cell studies, mutagenesis
- microfluidics, data analysis, microscopy.
Contact & link:
Paroi
Dynamics of bacterial cell wall
Research activities overview, related to antibioresistance:
We are exploring peptidoglycan structural modifications in various pathogenic Gram-positive bacteria in the frame of collaborations (ANR-funded or intra-Micalis) to decipher the molecular basis of
- β-lactam resistance in Clostridioides difficile (collab. Johann Peltier, I2BC) and
- bacterial persistence in Listeria monocytogenes (VBNC state, collab. Alessandro Pagliuso, Epimic team) or in Staphylococcus aureus (small-colony variants, collab. Philippe Gaudu, MicrobAdapt team).
Expertise:
- Peptidoglycan structure analysis by LC-MS
- Biochemical analysis of cell wall polysaccharides
- Selection of spontaneous cell wall mutants in semi-liquid medium
- Molecular genetics
Main references related to antibioresistance:
- Peltier, J. et al. J Biol Chem. 2011, 286:29053-29062. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.259150.
- Carvalho, F. et al., bioRxiv, 2023, doi.org/10.1101/2023.11.16.566987
Contact & link:
Keywords : cell wall, peptidoglycan, Gram-positive bacteria, persistence
DynPhages
DYNPHAGES
Research activities overview, related to antibioresistance:
For bacterial pathogens exhibiting ever increasing levels of resistance to antibiotics, phages are becoming a serious alternative for treatment. The team isolated and characterized virulent phages against clinical isolates of Enterococcus faecalis, and more recently against E. faecium, a pathogen listed by the WHO for which new antibiotics are urgently needed. We also have expertise in evolution experiments to enlarge phage host range, as most natural phages infect only few strains within a given species. As virulent phages are not available for all pathogens, a new approach consists in using temperate phages and derive mutants that only perform lytic cycles. The team’s long-standing expertise in temperate phages of Escherichia coli has led us to characterize atypical lytic induction cycles, in order to broaden our knowledge of the lysis/lysogeny control in temperate phages, and thus optimize the chances of success in creating efficient « lytic » mutants.
Expertise:
- Phage biology and genetic modification
- microbiology
Main references related to antibioresistance:
- Lossouarn J. et al. Viruses. 2019 Jan 10;11(1):48. doi: 10.3390/v11010048.
- Billaud et al. ISME Commun. 2021 Oct 25;1(1):55.
doi: 10.1038/s43705-021-00054-8.
Contact & link:
Keywords: phage-bacteria interactions; phage host range expansion; phage evolution; phage therapy; lysis-lysogeny
PhylHom
Phylogeny and Physiology of the Human Microbiome
Research activities overview, related to antibioresistance:
The PhylHom team focuses on interactions between the human microbiome and xenobiotic exposures ranging from diet to drug therapies and subsequent impact on microbial communities and human health across different stages of life. Current research activities related to antibioresistance include characterization of antimicrobial resistance elements microbiome from clinical cohorts and engineered systems. The team works on various antimicrobial resistance mechanisms induced by host-targeted drugs within the gut microbiome communities. The team also aims to develop nutritional strategies to modulate microbial metabolites to reduce abundance of antimicrobial resistance genes in the human gut.
Expertise:
- Anaerobic microbial ecology
- Multi-omics
- Microbial physiology
- Exposome
- Host-microbe interactions
Main references related to antibioresistance:
- Carbonnel, F., et al. « P900 A proof-of-concept, placebo-randomized controlled trial targeting adherent and invasive escherichia coli (aiec) with antibiotics in crohn’s disease: the teorem trial. » Journal of Crohn’s and Colitis 18.Supplement1 (2024): i1650-i1650.
- Aires, Julio, et al. « Occurrence of Neonatal Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Premature Neonates and Gut Microbiota: A Case–Control Prospective Multicenter Study. » Microorganisms 11.10 (2023): 2457.
- Luo, Yi-Hao, et al. « Increased expression of antibiotic-resistance genes in biofilm communities upon exposure to cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) and other stress conditions. » Science of The Total Environment 765 (2021): 144264.
Contact & link:
Keywords: Pharmaceuticals, resistome, gene transfer, microbial communities, exposome
PIMs
Pathogènes, Immunité et Microbiote
Research activities overview, related to antibioresistance:
The PIMs (Pathogens, Immunity and Microbiota) team is expert in the study of bacterial resistance to the host immune system. We characterize on one hand, the effects of the immune response on pathogenic bacteria in a pathobiome context, and on the other hand we develop new strategies to combat bacterial infections, mainly of the ESKAPE group (ie, K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginisa, E. coli) for which the WHO has recently pointed an alarming antibio-resistance issue. Promising drug candidates are currently tested for safety to the host and for activity against serious threat pathogens.
Finally, we develop communication means to increase reach out and large public awareness.
Expertise:
- Microbiology Gram
- Gram –Host/pathogen interaction
- Drug discovery
Main references related to antibioresistance:
- Patent n°EP3868376, 2021 N. Ramarao*, et al. Method of treating bacterial infections and pharmaceutical composition for treating bacterial infections.
- Leclerc M*, et al and Ramarao N*. Nitric Oxide Impacts Human Gut Microbiota Diversity and Functionalities. mSystems. 2021 Sep 14:e0055821
- SL. Tran, et al and N. Ramarao*. An anti-virulence drug targeting the evolvability protein Mfd protects against infections with antimicrobial resistant ESKAPE pathogens. In revision. Biorxiv : MS ID#: BIORXIV/2024/576688
Contact & link:
ProbiHote
Commensal and Probiotic Microorganisms-Host Interactions
Research activities overview, related to antibioresistance:
Our team is leader in the identification of probiotic and commensal bacteria with potential beneficial effects on the host, including antimicrobial effects. Our team is also at the forefront of the development of genetically modified bacteria able to produce and deliver therapeutic molecules, including antimicrobial peptides (AMPs). This application paves the way for the use of these microorganisms (known as Next-Generation Probiotics or NGPs) for the controlled production of the AMP of interest in situ. This strategy would solve: i) the replacement of the excessive use of antibiotics, ii) the problem of the cost of AMPs production and iii) the delivery to the site of infection.
Expertise:
- Traditional probiotics
- next-generation probiotics as recombinant bacteria
Main references related to antibioresistance:
- Mathieu E. et al. Nutrients. 2023 Jan 4;15(2):263. doi: 10.3390/nu15020263.
- Carvalho R. et al. Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 10;8(1):15072. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33469-w.
Contact & link:
ProCeD
Prokaryotic Cell Development
Research activities overview, related to antibioresistance:
- Identifying potential novel targets through the mechanistic study of essential processes (cell envelope biogenesis) on bacterial models (Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli) and pathogens (Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Streptococcus pneumoniae)
- Studying the mode of action of antibiotics inhibiting peptidoglycan synthesis
- Resensitization of Gram-negative pathogens to the last resort antibiotic colistin
- Identification of potential new antimicrobial compounds by screening for inhibitors of essential components of the cell wall synthesizing machineries
Expertise:
- far-end fluorescence microscopy
- bacterial cell biology and physiology
- bacterial genetics-screens
- genomics, transcriptomics, interactomics
- Bacillus subtilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
Main references related to antibioresistance:
- Tunç et al, Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2024. Jan 17;13(1):e0087423. doi: 10.1128/mra.00874-23
- Cornilleau et al, BioRxiv 2023, doi: 10.1101/2023.01.23.525174
- Zhang et al. BioRxiv, 2023, doi: 10.1101/2023.02.03.526509
Contact & link: